ISO/IEC 7816-12:2005 is Smartcard that provide a USB interface.
Jun 27th 2024
ISO/IEC 7816-12:2005 is Smartcard that provide a USB interface. This document is part of a broader series, ISO/IEC 7816, which outlines various aspects of IC cards used for identification and information exchange. Here is a detailed description of ISO/IEC 7816-12:2005:
Scope and Purpose
This part of ISO/IEC 7816 specifies the operating conditions of an integrated circuit card that provides a USB interface. Figure 1 shows the assignment of the contact fields for a USB interface and - to illustrate interoperability - the assignment as used in ISO/IEC 7816-3. Figure 1 — Assignment of contacts for a USB integrated circuit card
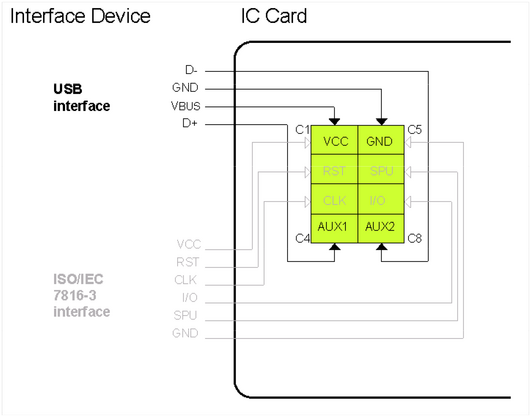
ISO/IEC 7816-12:2005 focuses on IC cards with contacts that use a USB electrical interface and defines the related operating procedures. It is designed to ensure interoperability between USB-ICC (USB Integrated Circuit Cards) and host systems by specifying the assignment of contact fields and operational protocols.
Structure of the Document
The document is divided into several sections, each detailing specific aspects of USB-ICC operation:
- Scope: Outlines the purpose and coverage of the standard.
- Normative References: Lists essential references and documents required for applying the standard.
- Terms and Definitions: Provides definitions for terms and abbreviations used throughout the document.
- Electrical Characteristics of the Contacts: Specifies the electrical requirements and contact assignments for USB-ICC.
- USB-ICC Operated by an Interface Device: Details the interface device requirements for operating a USB-ICC.
- USB Descriptors: Describes the standard and class-specific USB descriptors used by USB-ICCs.
- Data Transfer Between Host and USB-ICC: Explains the data transfer mechanisms, including bulk, control, and interrupt transfers.
Key Features
Electrical Interface
The standard defines the electrical characteristics for the USB contacts on the IC card, ensuring that the USB-ICC can operate correctly without being damaged when activated under different conditions (USB or ISO/IEC 7816-3).
USB Descriptors
USB descriptors play a crucial role in identifying the USB device and loading appropriate drivers. The document specifies various standard descriptors, including device, configuration, interface, and endpoint descriptors, which are read by the host during enumeration.
Data Transfer Protocols
The standard supports multiple data transfer types:
- Bulk Transfers: Used for commands, responses, and data exchange between the host and the USB-ICC.
- Control Transfers: Utilize the default control pipe for low-speed functions, with two implementation versions (A and B) that provide flexibility in handling different control requests.
- Interrupt Transfers: Optional transfers used for specific event notifications from the USB-ICC to the host.
Error Handling and Status Reporting
The document outlines mechanisms for reporting status and handling errors during data transfer. This includes detailed error codes and status bits that help in diagnosing issues related to the USB-ICC and the commands being processed.
Implementation and Compatibility
ISO/IEC 7816-12:2005 ensures that USB-ICCs are compatible with standard USB hosts and hubs, providing guidelines for interface devices to support USB-ICC operations. The standard also addresses potential patent rights and licensing issues, ensuring that manufacturers can implement the specifications without infringing on existing patents.
Annexes
The document includes several informative annexes:
- Annex A: Notation for state diagrams.
- Annex B: Scenarios for USB transfers.
- Annex C: Terms and definitions in the USB specification.
- Annex D: Class-specific descriptor for the Smart Card device class.
Conclusion
ISO/IEC 7816-12:2005 provides a comprehensive framework for the integration and operation of IC cards with USB interfaces. By adhering to this standard, manufacturers can ensure that their USB-ICCs will function reliably and interoperably within a wide range of host environments, facilitating secure and efficient data exchange for identification purposes.